There are many questions that emerge in the minds of patients when they first hear the words overactive thyroid. Some of these questions include what is the thyroid? why is it being described as overactive? and what are the implications if one is diagnosed? Additionally some may wonder about how a diagnosis is arrived at.
Here are some answers.
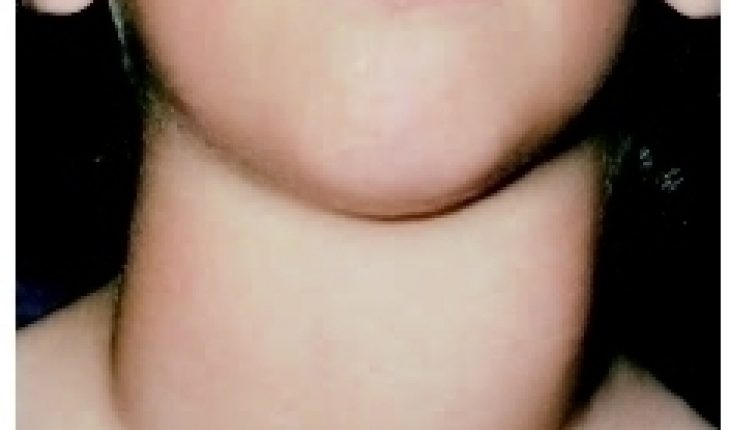
The thyroid in the human body is an endocrine gland. It is located in the neck (in front of the windpipe). The thyroid releases hormones into the blood stream. These hormones are actually chemicals that help the body to regulate the functions of the cells and organs. Overactive thyroid is also called hyperthyroidism. It is a condition which occurs when the thyroid gland works too hard and ends up producing too much thyroid hormone. This increases the speed of bodily functions leading to symptoms such as anxiety, weight loss and shaking.
Symptoms
These include feelings of nervousness or irritability, shaking, insomnia or poor sleeping patterns, intolerance or profuse sweating, muscle weakness and fatigue. In addition, if an individual has an increased appetite and is losing weight, an overactive thyroid may be the cause. Increased heart rate, irregular periods and sub fertility, diarrhea, shortness of breath, swollen and red eyes or double vision, loss of hair or thinning of hair strands and a swollen thyroid gland (goiter) are also symptoms of this condition.
Causes
Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disease that can cause hyperthyroidism. This condition occurs when antibodies from the immune system attack the body. In Graves’ disease, the antibodies imitate the behavior of TSH, and this causes the thyroid gland to make excess quantities of thyroid hormone, thereby leading to hyperthyroidism symptoms. It should be noted, though, that not all individuals with Graves? disease will have an overactive thyroid.
Nodular Thyroid Disease
Nodular thyroid disease occurs when small lumps or nodules in the thyroid gland cause hyperthyroidism. This happens because abnormal thyroid tissues in these nodules produce too much thyroid hormone.
Other Causes
The other causes are less prevalent. One such cause is an inflamed thyroid gland referred to as Thyroiditis. A viral infection or an autoimmune attack may case this condition. Pregnant women are more likely to face this condition.
High iodine intake (often through medicine) may also lead to overactivity in the thyroid. This is so since the thyroid gland uses iodine to make thyroid hormones.
Diagnosis
After an evaluation of the symptoms and physical examination, the doctor will likely order a blood test for the patient. This blood test should reveal the levels of thyroid hormones in the body. If the blood tests confirm that the patient’s thyroid is overactive then the doctor will refer the patient to an endocrinologist. Radioisotope scan which is also known as a radionuclide scan may help in the diagnosis of this condition. An overactive thyroid may be caused by one of or a combination of several factors. This condition tends to hamper the normal life of the affected individual. Modern medicine has, however, devised means of diagnosis and treatment that make this illness less threatening.