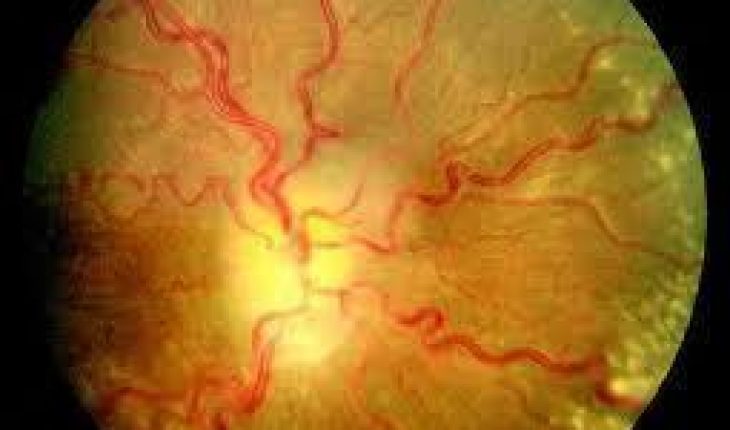
Pseudotumor cerebri is caused when pressure inside the skull, or intracranial pressure increases without apparent reason. Symptoms are similar to the symptoms of a brain tumor, hence the name “pseudo”- which means false, tumor cerebri. Pseudotumor cerebri can affect both adults and children, and occurs more frequently in women, and especially in obese women. If there is no obvious explanation for the Pseudotumor cerebri, the condition may also be referred to as idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Intracranial pressure associated with Pseudotumor cerebri may result in the distension of the optic nerve that usually leads to loss of vision. There are, however, medication that can alleviate the pressure behind the optic nerve but in many cases, surgery is required to reduce intracranial pressure.
Symptoms
Pseudotumor cerebri symptoms may include:
- Headaches- these may be either moderate, or severe and tend to originate behind the eyes, and will worsen with even the slightest movement of the eyes.
- Ringing in the ear.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Dizziness
- Pain in the neck, shoulder or back.
- Blurred vision.
- Visual obscuration (periods of blindness affecting one or both eyes and lasting seconds).
- Diplopia (double vision).
- Photopsia (seeing flashes of light).
Causes
The exact cause of Pseudotumor cerebri is unknown in the majority of cases, but doctors theorise that there is a link between Pseudotumor cerebri, and excessive quantities of cerebrospinal fluid inside the skull. This fluid helps to protect the tissues in the brain. It is thought that intracranial pressure occurs when there is a breakdown in the absorption process in the brain.
Risk factors
- Obesity- Pseudotumor cerebri occurs in 1 in every 100,000 people but the risk triples exponentially in obese women under 40.
- Medications- These substances could increase the risk of getting Pseudotumor cerebri.
- Growth hormones
- Oral contraceptives
- Tetracycline
- Discontinuing the use of Steroids
- Excessive use of Vitamin A
- Health concerns- These include Addison’s disease, head injury, kidney disease, lupus, Lyme disease, mononucleosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, sleep apnea, and an underactive parathyroid gland.
Treatment
Drugs are usually the first treatment options in patients with Pseudotumor cerebri symptoms. The drugs used in the treatment of Pseudotumor cerebri include glaucoma medication, or drugs that helps to decrease the level of cerebrospinal fluid production. These drugs do, however, have side effects. Side effects may include upset stomach, tiredness, tingling in the mouth, fingers and toes, and kidney stones. Diuretic drugs are also used to reduce the risk of cerebrospinal fluid buildup. If, however, the vision deteriorates even after these drugs, surgery is the only option that can alleviate the pressure behind the optic nerve. Surgical options include Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration, where a cut is made in the optic membrane, so the excess fluid can seep out. There is also Spinal fluid shunt surgery, where a tube or shunt is inserted into the brain, or into the lower spine to drain the excess cerebrospinal fluid there.